LayerZero emerges as a groundbreaking force in blockchain technology, serving as a layer-zero solution that enhances secure and efficient cross-chain communication. This interoperability protocol forges connections across a vast network of over 50 blockchains, enabling developers to create innovative omnichain applications, tokens, and user experiences that are second to none. By incorporating Oracle and Bridges technology within a trust-centric framework, LayerZero not only fosters a thriving ecosystem of decentralized finance and gaming projects but also represents a monumental leap in achieving a cohesive blockchain ecosystem.
LayerZero’s ascent as a distinctive force in the quest for blockchain interoperability has been marked by its immutable endpoints and permissionless executors, positioning it as a layer zero innovator. This platform excels in the secure transmission of messages, embodying the core tenets of blockchain technology—decentralisation and censorship resistance. The following sections will explore LayerZero’s unique technical architecture, how its omnichain approach sets it apart from other interoperability solutions, and the ambitious path this trailblazing LayerZero scan technology is carving in the dynamic blockchain domain.
Table of Contents
Understanding LayerZero
At the heart of LayerZero’s pioneering role in blockchain interoperability lies its unique technical architecture, which sets the Layer Zero Network apart from other interchain operability contenders. This section will dissect the essential components and the visionary outlook of LayerZero, highlighting its distinctive place in the blockchain landscape.
Technical Architecture
LayerZero’s Technical Architecture is a sophisticated framework designed to bolster the LayerZero protocol, enhance blockchain interoperability, and facilitate seamless communication across different networks. Here are the key components that form the backbone of LayerZero’s architecture:
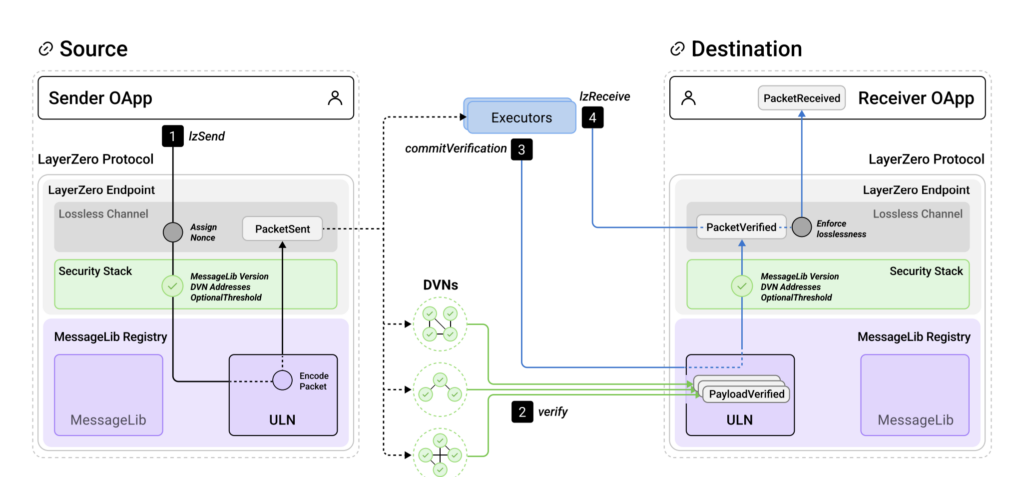
- Endpoints: LayerZero endpoints are smart contracts deployed on each supported blockchain, acting as the entry and exit points for messages sent across the LayerZero protocol network. They are immutable and non-upgradeable, providing a secure foundation for the protocol.
- Validation Libraries: The LayerZero endpoint libraries are integral to the protocol, containing the logic necessary to validate the messages being transferred. They ensure that the messages maintain consistency and accuracy across all chains involved.
- Decentralized Verifier Networks (DVNs): Introduced in LayerZero V2, the LayerZero endpoint DVNs are responsible for verifying the authenticity of messages. Operating independently, they add an additional layer of security and decentralisation to the message verification process.
- Executors: Executors within the LayerZero protocol are entities that carry out the instructions contained within the messages. In LayerZero V2, executors are designed to be permissionless, allowing anyone to participate in executing transactions, which aligns with the decentralised nature of blockchain.
LayerZero’s architecture differentiates itself from other interoperability solutions through its unique approach to message verification and transaction execution within the LayerZero protocol. - Modular Verification (X of Y of N): The LayerZero protocol’s Stargate method allows for a flexible and secure verification process by enabling multiple verification methods to be used together. It decouples execution from verification, which enhances the protocol’s security and adaptability.
- Horizontal Composability: By enhancing programmability and allowing unordered delivery of messages, the LayerZero protocol supports horizontal composability. This feature empowers applications to interact across different chains without being bound by transaction sequences, fostering a more efficient cross-chain communication environment.
- Permissionless and Modular: The design of the LayerZero protocol encourages a permissionless ecosystem by enabling anyone to operate the verification and execution entities. Its modular framework simplifies the integration of new functionalities or additional chains, enhancing the protocol’s adaptability and reach.
Looking ahead, LayerZero is positioned for significant growth and adoption. - Scalability and Adaptability: The LayerZero protocol is engineered with a future-proof focus, ensuring that applications developed on its foundation are scalable and can effortlessly adapt to upcoming technological advancements, thereby securing their long-term viability and effectiveness.
- Unified Applications: Developers can harness the power of the LayerZero protocol to craft applications that operate smoothly across multiple blockchains. This flexibility allows for the customization of security parameters to meet the specific requirements of their applications, ensuring both functionality and security.
- Enhanced Security ModelThe introduction of DVNs and Executors in LayerZero V2 marks a significant enhancement in addressing security concerns, presenting a fortified and flexible architecture for cross-chain communication that solidifies the LayerZero protocol’s position as a leader in the field.
At its core, the technical architecture of LayerZero fosters a more interconnected and agile financial ecosystem. It lays the groundwork for cutting-edge solutions in blockchain interoperability, with tools like layerzero scan enhancing transparency and trust.
LayerZero’s Role in Decentralized Finance (DeFi) and NFTs
LayerZero’s involvement in decentralized finance (DeFi) and non-fungible tokens (NFTs) is diverse, with its cutting-edge technical framework supporting a variety of applications that are reshaping the digital assets and financial services sectors. These key applications are becoming increasingly accessible through the LayerZero scan feature.
- Bridging:
- The core architecture of LayerZero is instrumental in bridging assets across blockchains, which simplifies the transfer of tokens, NFTs, and other digital assets with heightened security and efficiency, a process easily monitored through the LayerZero scan.
- Cross-chain Swaps:
- A number of decentralized exchanges (DEXs), including Sushi, Hashflow, WOO Network, and more, are utilizing LayerZero to enable multichain swaps. This integration allows users to seamlessly trade assets across various supported chains, a process that can be tracked using a LayerZero scan.
- Cross-chain Borrowing:
- Money market protocols are tapping into the technology of LayerZero to offer cross-chain borrowing services. This innovation boosts liquidity and access for users interested in lending and borrowing activities across multiple blockchains, with the LayerZero scan providing transparency and tracking for these operations.
- Omnichain Fungible Tokens (OFTs):
- Several multichain projects have converted their native tokens into Omnichain Fungible Tokens (OFTs) using LayerZero. These OFTs can be utilized across multiple blockchains, eliminating the need for wrapped versions or separate bridged tokens, and their movements can be followed through a LayerZero scan.
- Cross-chain Governance:
- LayerZero, a key player in the layer zero ecosystem, empowers cross-chain governance mechanisms. This innovation allows decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) and various governance structures to extend their reach across multiple blockchains through LayerZero scanning, fostering more inclusive and widespread governance decisions.
- Omnichain NFTs (ONFTs):
The advent of OFTs, powered by the layer zero framework, has revolutionized the NFT space by introducing ONFTs. These ONFTs can be traded, utilized, or showcased across diverse blockchain networks via LayerZero scan, heralding new opportunities for creators and collectors alike.
The LayerZero protocol’s technical architecture, which includes endpoints, ultra-light nodes, and a dual Oracle and Relayer mechanism, distinguishes itself in the realm of interchain operability. Its design is modular, scalable, and adaptable, catering to both EVM and non-EVM chains. The future of LayerZero is ambitious, aiming to expand its network to support over 50 blockchains, which will empower developers to create omnichain applications free from the constraints of single-chain technologies.
Ecosystem and Adoption
Since its launch, the ecosystem of LayerZero has seen exponential growth, with a myriad of decentralized applications (DApps) and platforms adopting the Stargate LayerZero for its interoperability features. These integrations are a testament to the protocol’s robustness and its capacity to streamline cross-chain transactions.
- Stargate Finance As the inaugural dApp on LayerZero, Stargate Finance stands as a pivotal element of the LayerZero crypto ecosystem. This composable asset bridge facilitates single-transaction cross-chain liquidity transfers seamlessly, eliminating the need for intermediary tokens. With a robust total value locked (TVL) of $419 million, Stargate Finance has cemented its role as a cornerstone within the layerzero crypto network, enabling fluid transfers across major blockchains such as Ethereum, Binance Chain, Polygon, Arbitrum, and Optimism [1][26].
- Adoption by Major DeFi Projects: LayerZero’s innovative layer 0 blockchain technology is the foundation for several top-tier DeFi platforms, including Radiant Capital, which leads the pack with a TVL of $200 million. Projects like InterSwap and Hashflow are also leveraging this technology to create cross-chain decentralised exchanges that rival Uniswap, demonstrating LayerZero’s ability to underpin complex financial applications [26].
- NFT and DeFi Innovations: Expanding its reach into the NFT arena, LayerZero’s partnerships, such as with Holograph, leverage the protocol for minting and bridging holographic omnichain crypto NFTs. Additionally, Pontem Network, a DeFi hub on the Aptos blockchain, is utilising LayerZero to craft its suite of DeFi applications, adding depth to the protocol’s ecosystem [23] [26].
The impressive performance metrics and expanding user community highlight LayerZero’s success and underscore its potential for future growth, with layer zero and layer zero scan being integral to its operational transparency. - Operational Milestones: LayerZero has achieved remarkable milestones, successfully transmitting over 87 million messages and processing transactions exceeding $40 billion. Boasting over 31,000 smart contracts on the Mainnet and maintaining a flawless security record with zero hacks, the protocol’s reliability and robustness are clear, further validated by layer zero and layer zero scans [5].
- User Engagement and Network ExpansionSupporting a diverse array of over 20 chains, including Ethereum, BNB Chain, Avalanche, Polygon, and Base, the LayerZero network has amassed 3 million independent users and a staggering 56 million transactions. These impressive statistics underscore LayerZero’s extensive influence and the escalating trust in its cutting-edge technology [25].
- Financial Backing and ValuationLayerZero has garnered significant financial backing, securing $261 million through three funding rounds and reaching a $2 billion valuation as of March 2023. This fiscal strength, combined with the support from industry giants like Sequoia, a16z, and Coinbase Ventures, underscores the market’s confidence in LayerZero Labs’ trajectory [4] [26].
The protocol’s partnerships and integrations reflect its commitment to advancing blockchain interoperability. - Strategic CollaborationsLayerZero’s alliance with Google Cloud to enhance their relayer services showcases the technological sophistication of the Layer Zero network. This partnership is a clear endorsement of LayerZero’s capabilities in facilitating dependable cross-chain transactions, further solidifying its position in the blockchain space. Additionally, the LayerZero scan tool is set to benefit from this collaboration, offering users enhanced visibility and tracking of their transactions.
Bridging Multiple Networks Layer Zero Bridge is at the forefront of LayerZero’s offerings, with projects like Aptos Bridge, BTC.B, and Testnet leveraging its technology to seamlessly connect different blockchain networks. This eliminates the need for creating additional chains, thereby streamlining liquidity movement and bolstering participation in DeFi applications across various ecosystems. The LayerZero bridge serves as a cornerstone in the company’s quest to simplify cross-chain interactions.
The LayerZero ecosystem stands as a beacon of technological innovation and a clear indicator of the protocol’s success in fostering widespread adoption. It’s not just a hub for cutting-edge tech but also a testament to Layer Zero’s influence in crafting a more interconnected blockchain landscape. With its robust technical framework and strategic alliances, LayerZero is poised to persist in its role as a trailblazer in the realm of cross-chain interoperability, with tools like LayerZero scan playing a pivotal role.
Security Measures and Trust Assumptions
LayerZero’s security measures are a critical aspect of its technical architecture, ensuring robust interoperability across blockchain transactions. The protocol employs a comprehensive security strategy, including layer zero and layer zero scan features, to maintain the integrity and reliability of cross-chain communications.
- Trust Assumptions and Independent Entities:
- The security model of LayerZero hinges on the independence of the Oracle and Relayer, with the protocol’s design assuming their honesty and non-collusion. By operating as independent entities, layer zero and layer zero scan mechanisms help preserve the system’s security integrity.
- To mitigate the risk of collusion, LayerZero enables user applications to select diverse Oracle/Relayer pair combinations, effectively spreading the risk and facilitating the use of their own relayers for a trust-minimized setup. This approach, integral to the layer zero framework, ensures enhanced security and is visible through layer zero scan tools [12].
- The security model of layer zero is further reinforced by granting user applications the flexibility to switch between Relayer and Oracle at any time. This dynamic capability redefines the security assumptions and diminishes the risk of reliance on a singular entity, a feature that can be monitored using a layer-zero scan [30].
- Decentralized Verifier Networks (DVNs) and Executors:
- LayerZero’s V2 iteration introduces DVNs and Executors, a strategic update that separates security from execution to bolster the protocol’s security architecture [22].
- The LayerZero protocol ensures operational continuity and resistance to censorship through the use of permissionless executors, while also implementing lazy nonce order enforcement to maintain the integrity of transactions [22].
- Applications leveraging the LayerZero protocol can customize their security by orchestrating various DVNs to create a specific set, granting privileged status to selected networks, and constructing their security stack, which encompasses the validation library, DVN set, block confirmations, and executor [22].
- Security Vulnerabilities and Economic Model Considerations:
- Despite its comprehensive security measures, Layer Zero has encountered criticism for its centralized security approach, particularly regarding the industry TSS Oracle and a relayer operated by Layer Zero itself, as highlighted by Layer Zero scan insights [31].
- Concerns about a potential ‘backdoor’ in the protocol’s code that could circumvent security measures have been raised, but LayerZero’s co-founder has addressed these by stating that developers hold the authority to configure settings that block any special access, ensuring the integrity of layer zero [32].
The LayerZero economic model, which is eagerly anticipated but not yet unveiled, stands as a critical element to scrutinize in order to fully ascertain the protocol’s robustness and the reliability of connections between oracles and relayers. LayerZero scan tools will be instrumental in monitoring these aspects [34].
The LayerZero protocol’s security framework is crafted to be both modular and flexible, empowering developers to tailor their security measures. This adaptability is key to addressing the dynamic hurdles within the blockchain interoperability arena.
Comparative Analysis with Other Interoperability Solutions
In the quest for blockchain interoperability, various solutions with unique architectures and methodologies are emerging. A comparative analysis underscores the distinctions and potential applications for each protocol, including those enabled by LayerZero and enhanced through LayerZero scan insights.
- Chainlink’s Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) vs. LayerZero:
- Security: CCIP, leveraging Chainlink’s robust infrastructure, may offer a more secure solution due to its integrated approach and the support of an anti-fraud network. In contrast, LayerZero’s network security, which can be monitored through a LayerZero scan, is still in the proving stages, with its model dependent on the autonomy of Oracles and Relayers.
- Interoperability: LayerZero stands out by supporting all blockchains with LZ endpoints, thus offering expansive interoperability options across various chains. CCIP’s interoperability, while currently confined to specific Chainlink cross-chain lanes, is being explored with Swift for transferring tokenized assets, signaling a strong future potential for interoperability that could be further assessed with LayerZero scan tools.
- Transaction SpeedLayerZero outperforms CCIP in transaction speeds, as CCIP is still undergoing testing. The LayerZero scan feature enhances the visibility and tracking of these transactions.
- Partnerships and Adoption: LayerZero has forged a strategic alliance with Google Cloud to bolster its relayer services, while Chainlink’s CCIP is exploring its potential with Swift, hinting at a future of broad adoption. The integration of LayerZero scan technology could further solidify its position in the market.
- Security: CCIP, leveraging Chainlink’s robust infrastructure, may offer a more secure solution due to its integrated approach and the support of an anti-fraud network. In contrast, LayerZero’s network security, which can be monitored through a LayerZero scan, is still in the proving stages, with its model dependent on the autonomy of Oracles and Relayers.
- Wormhole vs. LayerZero:
- Governance and Validators: While Wormhole’s transaction integrity relies on a centralised Guardian governance model, LayerZero secures its network through a decentralised blend of Oracles and Relayers. This approach, monitored by the LayerZero scan, ensures robust security.
- Validator Risk: The security of Wormhole hinges on a mere 19 validators, which poses a significant risk. Conversely, LayerZero’s security framework empowers user applications to choose diverse Oracle/Relayer pairings, fostering a trustless environment that can be monitored through a LayerZero scan.
- Governance and Validators: While Wormhole’s transaction integrity relies on a centralised Guardian governance model, LayerZero secures its network through a decentralised blend of Oracles and Relayers. This approach, monitored by the LayerZero scan, ensures robust security.
- Axelar vs. LayerZero:
- Blockchain Structure: Axelar operates on a Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) blockchain and leverages validators with its native token for message verification. In contrast, LayerZero boasts a modular, scalable architecture that supports EVM and non-EVM chains without requiring a native token for validator security, a process observable through the LayerZero scan.
- Operational Process: Axelar’s protocol entails the tracking of events, message verification, and the delivery of signed messages to a target chain’s gateway. LayerZero streamlines this process with ultra-light nodes and a dual Oracle/Relayer system, optimizing for modularity and gas efficiency with the added transparency provided by LayerZero scan.
- Blockchain Structure: Axelar operates on a Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) blockchain and leverages validators with its native token for message verification. In contrast, LayerZero boasts a modular, scalable architecture that supports EVM and non-EVM chains without requiring a native token for validator security, a process observable through the LayerZero scan.
- Layer Zero and Accumulate:
- Approaches to Interoperability: LayerZero and Accumulate represent two pioneering forces in the interoperability arena, each with unique methodologies. A theoretical partnership could significantly enhance cross-chain bridging efficiency and transparency, a development that would be closely followed using the LayerZero scan.
- Approaches to Interoperability: LayerZero and Accumulate represent two pioneering forces in the interoperability arena, each with unique methodologies. A theoretical partnership could significantly enhance cross-chain bridging efficiency and transparency, a development that would be closely followed using the LayerZero scan.
Selecting the right interoperability solutions from LayerZero will depend on the unique requirements of each application, taking into account aspects like security, speed, and the ability to interoperate, all while keeping up with the ongoing technological advancements. Bridging the divide between existing blockchain technologies and the sophistication of HTTP/HTML/XML levels of abstraction is critical for the blockchain industry’s progression, and LayerZero scan tools can play a significant role in this development.
Challenges and Critiques of LayerZero
In the quest for blockchain interoperability, various solutions with unique architectures and methodologies are emerging. A comparative analysis underscores the distinctions and potential applications for each protocol, including those enabled by LayerZero and enhanced through LayerZero scan insights.
- Debates on Security and Modularity:
- LayerZero’s commitment to modularity has ignited conversations around the choice between global and local security models. The protocol’s innovative design allows dApps to leverage their native tokens in securing validators, potentially revolutionizing each token into a proof-of-stake dApp, a concept closely examined by LayerZero scan [31].
- LayerZero’s novel tokenomics-based security strategy stands in contrast to other Layer 0 frameworks that might adhere to more conventional models. Developers’ preference for security design autonomy is a key factor when comparing LayerZero with alternatives such as Axelar, with the decision often informed by LayerZero scan insights [31].
- Economic and Cost Structure Concerns:
- The mechanics behind LayerZero’s value capture, which operates on a minimalist tokenless model, are yet to be clarified. This approach diverges sharply from protocols like Axelar, which have a more transparent value capture mechanism through their native token, AXL, as highlighted by the LayerZero scan [31].
- LayerZero’s pricing strategy suggests a compromise that benefits certain business models and types of transactions. The protocol’s reliance on a third-party oracle could lead to higher variable fees per transaction, a point that is often scrutinized through a LayerZero scan compared to the fixed costs seen in other solutions [31].
- Critiques and backlash:
- The recent surge in high-profile on-chain security incidents has underscored the importance of robust security measures, prompting a closer look at whether LayerZero’s modular design and customizable security options will resonate with developers and users. This scrutiny, intensified by LayerZero scan tools, raises the question of whether the platform’s features will be embraced within the blockchain community.
- Operated by LayerZero, the Goerli ETH marketplace has come under fire from Ethereum developers who are concerned that it might be capitalizing on a token without inherent value and limiting access to a crucial resource, potentially deterring fresh talent from contributing to the Ethereum ecosystem. These criticisms underscore the need for LayerZero scan capabilities to ensure transparency and trust.
- In defending the Goerli ETH market, some developers argue that it offers an extremely cost-effective solution and remind critics of the small paid transactions for Goerli ETH that predate the current debate. This discussion underscores the fine line LayerZero must tread in balancing innovation with maintaining community trust, a balance that could benefit from the insights provided by a thorough LayerZero scan.
LayerZero’s journey through the blockchain landscape is marked by challenges and critiques, emphasizing the critical nature of security, tokenomics, and cost structures. These elements are central to the ongoing discourse on blockchain interoperability and the future of decentralized applications, with LayerZero scanning playing a pivotal role in navigating these complex issues.
Conclusion
Our deep dive into LayerZero has revealed the intricate design of its technical architecture and the unique modularity that sets it apart from other interoperability solutions. The layer zero mission to interconnect over 50 blockchains is a testament to its crucial role in the evolution of decentralized applications and blockchain technology. By addressing key interoperability challenges, LayerZero scan not only enhances existing blockchain functionalities but also paves the way for a more cohesive blockchain ecosystem.
As LayerZero continues to evolve, its development and strategic partnerships are set to redefine the DeFi and NFT landscapes, making cross-chain collaboration the norm. With layer zero and LayerZero scan at the forefront, the platform is shaping a future where innovation thrives and community engagement is paramount, signaling an era of boundless cross-chain possibilities
FAQs
What exactly is Layer Zero?
LayerZero stands as a groundbreaking interoperability protocol within the layer zero space, providing a foundational connection for all blockchains. It champions the growth and innovation of the decentralized world by integrating new blockchains, each with their own distinct focus, vision, and utility, through a LayerZero scan.
Could you explain the messaging protocol used by LayerZero?
LayerZero boasts an immutable, open-source messaging protocol that is a cornerstone in the Layer Zero domain, enabling developers to craft omnichain, interoperable applications. Thanks to LayerZero scanning, this protocol facilitates the smooth transfer of data, the execution of external function calls, and token movements across various blockchains while ensuring applications retain their autonomy and control.
Which blockchain networks are compatible with LayerZero?
LayerZero offers compatibility with an extensive array of prominent blockchain platforms and layer 2 solutions, such as Ethereum, BNB Chain, Aptos, Avalanche, Polygon, Optimism, Arbitrum, and Base, to name a few. This interoperability positions LayerZero as a versatile tool for users seeking to navigate the blockchain ecosystem, and its functionality can be monitored using a LayerZero scan.
How does LayerZero differ from Layer 2 technologies?
In the context of the OSI model, LayerZero plays distinct roles at different layers:
- At Layer 1, it establishes a robust foundational infrastructure for the network.
- At Layer 2, it ensures a secure and dependable connection between devices.
- At Layer 3, it facilitates the movement of data throughout the network.
Distinct from Layer 2 scaling solutions, LayerZero operates at a foundational level, facilitating connectivity and seamless communication across diverse blockchain networks. This innovative approach underscores the unique position of Layer Zero in the blockchain infrastructure, with the LayerZero scan providing insights into its network activities.
References
[1]: https://www.ledger.com/academy/topics/crypto/what-is-layerzero
[2]: https://layerzero.network/
[3] – https://alexkat.medium.com/layerzero-trustless-omnichain-interoperability-protocol-a-deep-dive-51ffb28ed081
[4] – https://coinmarketcap.com/alexandria/article/what-is-layerzero-omnichain-protocol
[5] – https://www.notboring.co/p/layerzero-the-language-of-the-omnnichain
[6]: https://beincrypto.com/learn/layerzero-explained/
[7]: https://medium.com/layerzero-official/introducing-layerzero-v2-076a9b3cb029
[8]: https://medium.com/coinmonks/layerzero-the-first-omnichain-interoperability-protocol-for-cross-chain-communication-e5d5e37b99a9
[9]: https://www.coinspeaker.com/guides/what-is-layerzero-revolutionizing-omnichain-interoperability-protocol-explained/
[10] – https://www.ccn.com/layerzero-zro-explainer-what-is-omnichain-protocol/
[11]: https://medium.com/layerzero-official/layerzero-an-omnichain-interoperability-protocol-b43d2ae975b6
[12]: https://blog.li.fi/layerzero-a-deep-dive-6a46555967f5
[13]: https://medium.com/chainlight/ecosystem-explorer-exploring-interchain-operability-protocols-and-their-security-measures-0a21e195f732
[14]: https://accumulatenetwork.io/2022/04/comparing-web3-interoperability-solutions/
[15]: https://www.cryptoeq.io/articles/layerzero-interoperability-bridge
[16]: https://www.alphaplease.com/p/chainlink-ccip-layerzero-wars-crypto-web3
[17] – https://fivet.com/blogs/insights-publications/blockchain-interoperability-layerzero
[18]: https://medium.com/@codexchain/revolutionizing-blockchain-with-no-code-token-and-nft-integration-using-layerzero-technology-4ecf52291ba8
[19]: https://medium.com/layerzero-official/layerzero-v2-deep-dive-869f93e09850
[20]: https://layerzero.gitbook.io/docs/layerzero-v1/introduction
[21]: https://medium.com/momentum6/blockchain-interoperability-a-prevailing-need-in-the-industry-46ee3cbabcfc
[22]: https://layerzero.network/publications/LayerZero_Whitepaper_V2.pdf
[23] – https://blockchain.news/analysis/holograph-integrates-layerzero-to-facilitate-holographic-omnichain-nfts-that-beam-across-blockchains
[24]: https://www.coingecko.com/learn/layerzero-ecosystem
[25] – https://ld-capital.medium.com/ld-capital-layerzero-the-future-path-of-cross-chain-innovations-and-star-projects-8dd5e79312b2
[26] – https://cointelegraph.com/news/layerzero-s-multi-chain-ecosystem-grows-as-airdrop-hunters-ramp-up-their-efforts
[27] – https://pintu.co.id/en/academy/post/chainlinks-ccip-vs-layerzero-which-one-is-better
[28]: https://medium.com/@orderlynetwork/what-is-omnichain-in-crypto-a-beginners-guide-4d81c89afb11
[29] – https://composable-security.com/blog/secure-integration-with-layer-zero/
[30]: https://medium.com/l2beat/circumventing-layer-zero-5e9f652a5d3e
[31] – https://messyproblems.substack.com/p/the-three-debates-of-the-layer-zero
[32] – https://www.coindesk.com/tech/2023/01/30/bridge-platform-layerzero-denies-allegations-it-kept-backdoor-secret/
[33]: https://medium.com/@btslabs/layerzero-a-new-era-of-seamless-cross-chain-interoperability-d4223b8652ec
[34]: https://www.gate.io/learn/articles/firstvip-research-report-layerzero-an-omnichain-interoperability-protocol/1805
[35] – https://www.dlnews.com/articles/defi/layerzero-faces-backlash-after-monetising-valueless-ethereum-sandbox-tokens-goerli-testnet-bridge/
[36] – https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/cross-chain-interoperability-protocols-comparing-chainlinks-singh-eznec?trk=public_post_main-feed-card_feed-article-content
[37] – https://blog.crepe.fund/comparing-ccip-and-layerzero-handling-real-world-assets-rwas-in-blockchain-interoperability-d68e2d77405d