Bitcoin Ordinals herald a pioneering stride in blockchain technology, introducing an innovative method for the creation and trading of non-fungible tokens (NFTs) directly on the Bitcoin network. Launched in January 2023 by BTC mainnet developer Casey Rodarmor, this protocol represents a new system for permanently storing any type of data directly on Bitcoin’s blockchain, leveraging the foundational units of Bitcoin—satoshi—to facilitate the inscription of diverse data, including digital assets like images, videos, and meme tokens, onto the blockchain.
By embedding ordinals and metadata onto individual satoshis, Bitcoin Ordinals not only demystify the technical complexity surrounding NFTs on blockchain but also spotlight the versatility of Bitcoin’s decentralized database beyond its financial utility.This advancement underscores the intersection between blockchain’s robust consensus mechanisms and the burgeoning NFT market, presenting a unique canvas for digital ownership on the Bitcoin blockchain.
While preserving the core principles of decentralization and on-chain data integrity, the ordinals crypto innovation opens a new frontier for NFT enthusiasts and blockchain aficionados alike. As we navigate through this comprehensive guide, we will explore the mechanism of Bitcoin Ordinals, distinguish it from traditional NFT frameworks, and delve into its implications for the digital assets ecosystem, providing a thorough understanding of its operational ethos and the potential challenges it brings to the forefront of blockchain technology.
What Are Bitcoin Ordinals?
Bitcoin Ordinals represent a novel approach to utilizing the Bitcoin blockchain for more than just financial transactions. By applying ordinal theory, each satoshi, the smallest unit of Bitcoin, is assigned a unique number. This process, known as ordinal inscription, allows for the attachment of data like images, videos, or other digital content directly to individual satoshis.
Ordinal inscriptions transform these satoshis into unique and verifiable digital assets, effectively creating non-fungible tokens (NFTs) directly on the Bitcoin blockchain. Unlike traditional NFTs, which typically reference external data or links, everything about an Ordinal—be it an image, video, or any form of digital content—is stored directly on the blockchain. This method not only ensures the immutability and security inherent to Bitcoin but also enhances the assets’ resistance to censorship.
The creation of Bitcoin Ordinals and their inscriptions are facilitated by the Ordinals protocol, which was introduced on the Bitcoin mainnet in January 2023. This protocol assigns detailed information to the serial numbers of each satoshi, allowing them to carry additional content. As a result, each inscribed satoshi is not only a part of the financial database of Bitcoin but also serves as a carrier of unique digital content, marking a significant shift in how blockchain technology can be utilized for the creation and management of digital assets.
The impact of Bitcoin Ordinals on bitcoin users is multifaceted, with opinions divided on their benefits and drawbacks. Advocates argue that Ordinals enhance the Bitcoin network’s sustainability, security, and attractiveness to new developers, while critics raise concerns about resource misuse, increased transaction fees, and ethical issues, noting that users have limited options in opting out of this functionality.
The History and Development of Bitcoin Ordinal NFTs
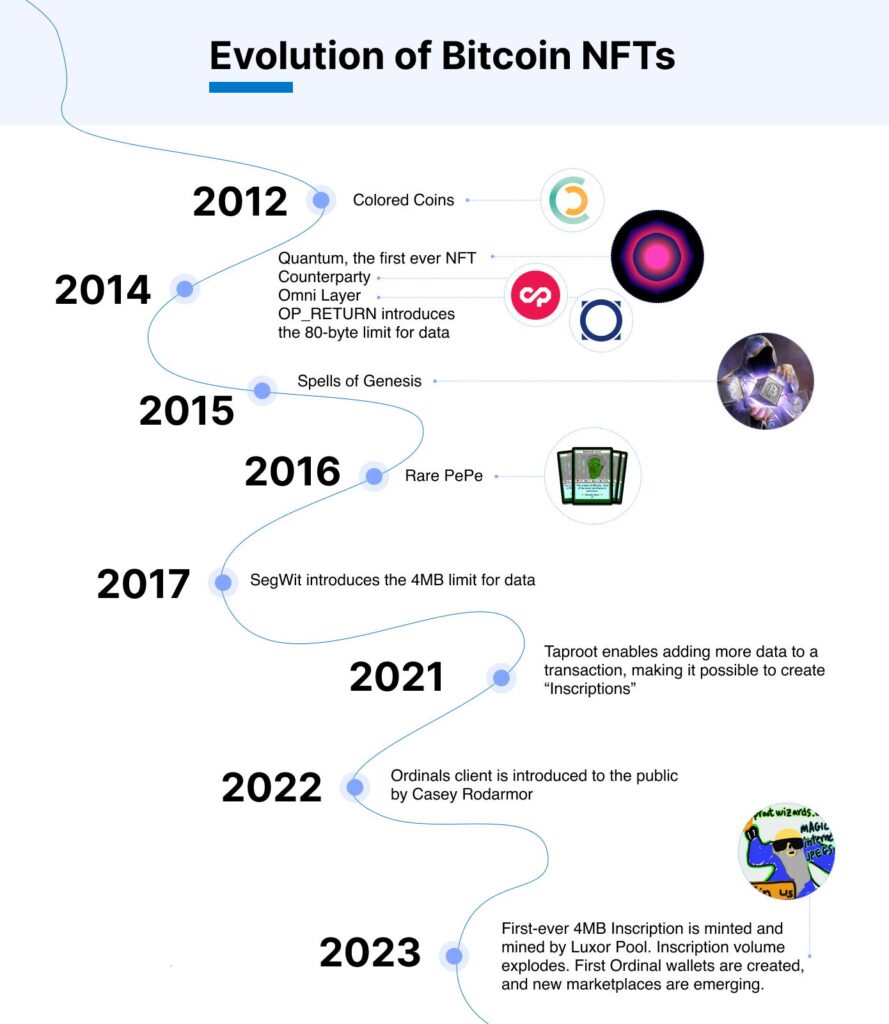
The inception of Bitcoin Ordinals can be traced back to significant updates on the Bitcoin network, primarily the Segregated Witness (SegWit) and Taproot upgrades. SegWit, implemented in 2017, was a pivotal update that introduced a soft fork of the Bitcoin blockchain. It segregated a Bitcoin transaction into two sections, significantly expanding the limits of how much arbitrary data one could include in a transaction. This laid the groundwork for more complex applications to be built on the Bitcoin network.
Following SegWit, the Taproot upgrade was launched on November 14, 2021. This update further enhanced the Bitcoin network’s capabilities by creating a more efficient system for storing arbitrary witness data. It relaxed the limitations on how much arbitrary data could be placed inside a Bitcoin transaction, paving the way for the development of new forms of digital assets on the Bitcoin blockchain. Bitcoin developers have voiced concerns about the effects of ordinals on network fees and congestion, requesting censorship action to take place.
The actual deployment of Bitcoin Ordinal NFTs occurred when developer Casey Rodarmor launched the Ordinals protocol on the Bitcoin mainnet on January 20, 2023. This marked a significant milestone as it allowed for the inscription of various types of digital content, including images and videos, directly onto individual satoshis. Since its launch, over 200,000 ordinal bitcoin NFTs have been minted, demonstrating the growing interest and application of this innovative technology.
How Do Bitcoin Ordinals Work?
Bitcoin Ordinals operate directly on the base Bitcoin blockchain, leveraging its security and permanence to create and store ordinal NFTs without the need for additional layers. The functionality of Bitcoin Ordinals hinges on the unique process of inscription, where data is permanently recorded on individual satoshis, the smallest units of Bitcoin. This section outlines the step-by-step mechanics of how Bitcoin Ordinals operate, emphasizing the technical aspects and tools involved in creating and managing these digital assets.
Step-by-Step Process of Creating Bitcoin Ordinals
Setting Up the Environment: The initial step involves downloading and syncing Bitcoin Core with the blockchain, ensuring that the node is fully operational.
Wallet Preparation: Users must then create an Ordinals-specific wallet that functions as a bitcoin wallet with a Taproot wallet address and ‘coin control’ features, essential for interacting with the Ordinals protocol. Magic Eden Wallet is highly recommended due to its comprehensive support for Ordinals, including these specific features, and native integration with the Magic Eden marketplace, which is pivotal for trading these assets. This noncustodial bitcoin wallet ensures users have the necessary tools to engage with Ordinals effectively.
Funding the Wallet: To activate the wallet, users need to transfer Bitcoin to their wallet’s RECEIVE address. This can typically be done through most centralized exchanges (CEXs).
Inscribing Data: With the wallet set up and funded, the next step is the actual inscription. Here, digital content such as images, videos, or texts is inscribed onto the satoshis. This data is stored within the witness part of a Bitcoin transaction, making each inscribed satoshi a unique and traceable digital asset.
Technical Details of Ordinals Inscription
Data Storage: Unlike traditional NFTs that may link to external data, all content associated with an Ordinal is stored directly on the blockchain, enhancing security and immutability.
Ordinal and Taproot Addresses: Users typically manage two types of Bitcoin addresses in their wallets—one for standard Bitcoin transactions and another dedicated to Ordinals and digital artifacts, known as a Taproot address.
Serialization and Mining: Each Ordinal is serialized based on the order it was mined, maintaining a precise record of ownership and origin within the blockchain’s immutable ledger.
Distinctive Features of Bitcoin Ordinals
Integration and Compatibility: Ordinals are fully integrated into the Bitcoin blockchain, unlike other NFTs that may operate on separate layers or utilize different consensus mechanisms like Proof of Stake (PoS).
Flexibility in Asset Type: The nature of an inscribed satoshi can vary from being fungible to non-fungible, depending on the specific content and the owner’s intentions, which introduces a flexible approach to digital asset classification.
This intricate process not only highlights the technical prowess required to manage Bitcoin Ordinals but also underscores the innovative use of blockchain technology to foster a new class of digital assets. Through these mechanisms, Bitcoin Ordinals are set apart from traditional NFTs, offering a unique method for digital expression and ownership directly on the Bitcoin network.
The Difference Between Bitcoin Ordinals and Traditional Non Fungible Tokens
Bitcoin Ordinals and traditional NFTs diverge significantly in their foundational technology and operational mechanisms. Traditional NFTs are primarily minted on blockchain platforms like Ethereum, utilizing smart contracts to manage the ownership and transfer of digital assets. These smart contracts facilitate the representation of digital art and collectibles, embedding metadata or URLs that point to external data sources. In contrast, Bitcoin Ordinals are inscribed directly onto the Bitcoin blockchain, leveraging updates such as Segregated Witness (SegWit) and Taproot to embed data onto individual satoshis, the smallest denomination of Bitcoin.
The inscription process for Bitcoin Ordinals introduces a unique approach to asset fungibility. While traditional NFTs on platforms like Ethereum are distinctly non-fungible from the outset, Bitcoin Ordinals maintain the fungibility of satoshis until they are inscribed. Once inscribed, these satoshis transform into non-fungible assets by assigning unique numbers and embedding data directly onto the blockchain. This method ensures that all content related to the Ordinal, whether it be images inscribed data, videos, or other forms of digital media, is stored immutably on-chain.
Furthermore, the scalability and economic model of Bitcoin Ordinals differ markedly from traditional NFTs. Without the need for smart contracts, Bitcoin Ordinals do not facilitate creator royalties, a common feature in the Ethereum-based NFT ecosystem. This not only affects the potential earnings for creators but also simplifies the transaction process by eliminating complex contract interactions. Additionally, the inherent properties of the Bitcoin blockchain—immutability, decentralization, and robust security—are retained in Bitcoin Ordinals, providing a secure and transparent environment for digital ownership.
Bitcoin NFTs, represented through the Bitcoin Ordinals, differ from non-Bitcoin NFTs by utilizing the concept of ordinals and inscriptions to create unique digital assets directly on the Bitcoin blockchain, highlighting a distinct approach from the smart contract-based NFTs on platforms like Ethereum.
Applications and Use Cases for Bitcoin Ordinal NFTs
Bitcoin Ordinals introduce a versatile platform for various applications beyond traditional financial transactions. Digital artists, for instance, leverage this technology to inscribe their artwork directly onto satoshis, ensuring that their creations are secured by the robust Bitcoin blockchain. This not only enhances the security and immutability of digital art but also opens up new avenues for artists to monetize their work directly through blockchain technology.
In the realm of gaming, Bitcoin Ordinals have carved out a niche by enabling the creation of unique in-game items that are fully decentralized and immutable. These items, once inscribed onto satoshis, provide gamers with true ownership, a significant shift from traditional online gaming models where items are typically controlled by game developers. This innovation not only enhances the gaming experience but also introduces a new economic model within the gaming industry, where players can trade or sell their in-game assets as they would physical goods.
The utility of Bitcoin Ordinals extends into more practical applications such as data storage and intellectual property management. For example, scientific data, election results, and professional certifications can be recorded on the blockchain, providing a tamper-proof and transparent method for data management. Similarly, in the intellectual property domain, Bitcoin Ordinals offer a revolutionary approach to managing copyrights, reducing disputes and ensuring that ownership rights are clearly defined and permanently recorded on the blockchain.
These applications demonstrate the broad potential of Bitcoin Ordinals to impact various industries by providing a secure, immutable, and decentralized platform for both creative expressions and practical data management.
How to Buy, Sell, and Trade Bitcoin Ordinals
To engage in the buying, selling, and trading of Bitcoin Ordinals, users must navigate a specific set of platforms and tools designed to support these unique digital assets. Here is a detailed guide on the process: It’s crucial to select wallets that support bitcoin ordinals, given the currently limited number of wallets that offer this capability, to ensure seamless transactions within the Ordinals ecosystem.
Selecting the Right Bitcoin Wallet for Ordinals
Due to the specialized nature of Bitcoin Ordinals, most conventional Bitcoin wallets do not support the Ordinals protocol. For those interested in engaging with Bitcoin Ordinals, it is essential to select a compatible wallet. Three prominent wallets that facilitate the handling of Bitcoin Ordinals include Ordinals Wallet, Xverse, and UniSat. These wallets are specifically designed to interact with the Ordinals protocol, providing the necessary infrastructure to manage and trade Ordinals effectively.
Participating in Marketplaces
Once the appropriate wallet is set up, users can participate in marketplaces that support the trading of Bitcoin Ordinals. Notable marketplaces such as Ordinals Wallet and OKX offer platforms where users can buy, sell, and trade these NFTs. Additionally, upcoming platforms like Magic Eden are expanding their services to include a dedicated Rune Marketplace, set to launch on April 23rd, enhancing the accessibility and variety of Bitcoin Ordinals available to enthusiasts.
Transaction Process
The process of buying Bitcoin Ordinals typically starts by selecting the desired Ordinal on the marketplace. Users must connect their compatible wallet, such as Xverse, to the marketplace platform. For instance, on Magic Eden, users would click “Connect Wallet,” select their wallet app, and then browse available Bitcoin Ordinals. Upon choosing an Ordinal, users can proceed to purchase by confirming the transaction. The Bitcoin Ordinal will then appear in their wallet, usually within about 10 minutes, completing the acquisition process.
For sellers, a key aspect of the process involves listing their Bitcoin Ordinals on the marketplace. This is usually done by navigating to the assets section of their wallet, selecting the Ordinals they wish to sell, and clicking on the list button. The marketplace then displays the Ordinal for other potential buyers to view and purchase.
These steps outline the fundamental processes involved in buying, selling, and trading Bitcoin Ordinals, leveraging specific tools and platforms designed to accommodate the unique requirements of these digital assets.
Top Bitcoin Ordinals NFT projects
The Bitcoin Ordinals ecosystem has witnessed the emergence of several groundbreaking NFT projects, each contributing uniquely to the digital collectibles space on the Bitcoin blockchain. Here we highlight some of the most notable projects based on their innovation, market impact, and artistic value.
Notable Collections and High-Value Transactions
The Ordinal Market has seen collections such as Original Maxi Beast reaching significant milestones, with individual pieces valued at 1 Bitcoin. Similarly, the Flar collection has experienced a dramatic 200% increase in value, now priced at 0.9 Bitcoin. Among the high-value transactions, the sale nft collection of six alien monkeys stands out, fetching over 53 Bitcoin, approximately $3 million, underscoring the high stakes and investor interest in this burgeoning market.
Upcoming and Established Projects
Several projects are shaping the landscape of Bitcoin Ordinals. King Art’s upcoming collection is highly anticipated by crypto community and is expected to include exclusive pieces available for early supporters through a whitelist. Another intriguing project is Inconceivable on Bitcoin, which plans to launch a 10,000-piece collection, notable for its relatively low mint price below $500, making it accessible to a broader audience. Taproot Wizards is another creative endeavor, featuring 2,106 unique digital wizards, each with distinct designs and attributes, showcasing the artistic diversity possible within the Ordinals framework.
Unique and Thematic Collections
Ordinal Punks and Bitcoin Frogs represent thematic collections that have captivated the community. the first Ordinal Punks, a limited series of 100 profile picture (PFP) art pieces, draws inspiration from the iconic CryptoPunks and adapts it within the Bitcoin ecosystem. Bitcoin Frogs includes 10,000 unique frog collectibles, each minted directly on the Bitcoin blockchain, combining whimsy with the security and permanence of blockchain technology. These collections not only highlight the creative potential of Ordinals but also demonstrate how traditional NFT concepts can be reimagined on Bitcoin.
These projects exemplify the dynamic and evolving nature of the Bitcoin Ordinals space, each contributing to the digital landscape in unique ways, from high-value transactions and significant collection values to innovative artistic contributions and thematic explorations.
The Impact of Bitcoin Ordinals on the Bitcoin Ecosystem
Bitcoin Ordinals have introduced a transformative layer to the Bitcoin blockchain, enhancing its utility by enabling the storage and trade of digital art and other digital assets directly on the blockchain. This innovation has attracted a larger audience, which has led to increased transaction fees and a backlog of transactions, with the average confirmation time rising from 30 minutes to 25 hours. Despite these challenges, the ability to integrate digital assets directly onto the Bitcoin blockchain has opened up new use cases and attracted new user groups, such as artists and content creators, potentially increasing the blockchain’s value and utility.
The introduction of Bitcoin Ordinals has also sparked a significant debate within the Bitcoin community. Some core developers and users see Ordinals as an innovative way to expand Bitcoin’s functionality, making it more sustainable by creating more demand for block space. Others, however, argue that it represents a misuse of the network’s resources, leading to unnecessary strain and increased transaction costs. This division underscores the broader impact of Bitcoin Ordinals on the blockchain ecosystem, highlighting both the potential benefits and the challenges they introduce.
Furthermore, the Taproot upgrade has played a crucial role in facilitating the adoption of Bitcoin Ordinals by enhancing transaction efficiency and privacy. This upgrade allows complex transactions to appear as standard transactions, reducing the amount of data needed and consequently lowering transaction costs. This technical advancement supports the broader adoption of Bitcoin Ordinals, enabling more sophisticated applications on the blockchain and potentially driving further innovation and development within the crypto ecosystem.
Challenges and Controversies Surrounding Bitcoin Ordinals NFTs
The introduction of Bitcoin Ordinals has sparked significant debate within the cryptocurrency community, highlighting a divide between traditionalists and innovators. Critics such as Max Keiser and Luke Dashjr have labeled Bitcoin Ordinals as spam, arguing that they overload the network with unnecessary data. This sentiment is echoed by other traditionalists who believe that the Bitcoin blockchain should be reserved solely for peer-to-peer transactions. Concerns have been raised about the misuse of Bitcoin scripts that created over 70,000 individual satoshis with negative values, rendering them untradeable and effectively dormant.
The operational impact of Ordinals on the Bitcoin network has been profound, with increased block congestion and slower settlement times due to the embedding of arbitrary data. This has led to a surge in transaction fees, with the average fee increasing by up to 25 times over the past year. Such developments have fueled discussions about the sustainability of the network, with some community members worrying that rising fees could push ordinary users away from using Bitcoin for daily transactions.
Moreover, the controversy surrounding Bitcoin Ordinals has raised the specter of a potential Bitcoin fork, reminiscent of past disagreements over protocol rules and block size. This division within the community not only highlights the challenges of integrating new technologies into established systems but also underscores the ongoing evolution of blockchain technology as it adapts to new use cases and market demands.
Conclusion
The exploration of Bitcoin Ordinals illuminates a significant evolution within the blockchain ecosystem, marrying the foundational principles of Bitcoin with the burgeoning world of NFTs. By enabling the direct inscription of digital content onto individual satoshis, Bitcoin Ordinals redefine the scope of what’s possible within the Bitcoin network. This breakthrough not only extends the utility of Bitcoin’s history well beyond a mere currency but also opens up a novel avenue for artists, developers, and consumers to engage with digital assets in a secure, immutable manner.
As the community and technology around Bitcoin Ordinals continue to evolve, so too will the applications and implications of this innovative protocol. The emergence of Bitcoin Ordinals has catalyzed a vibrant ecosystem of digital art, collectibles, and beyond, setting the stage for further exploration and development. Amidst debates and challenges, the integration of NFTs on Bitcoin’s blockchain stands as a testament to the unending drive towards innovation in the crypto space. The journey of Bitcoin Ordinals from a conceptual novelty to a significant cryptographic milestone underscores the dynamic, ever-evolving nature of blockchain technology and its capacity to continuously redefine the boundaries of digital ownership and creativity.
FAQs
1. How do Bitcoin Ordinals differ from traditional NFTs?
Bitcoin Ordinals differ from traditional NFTs primarily in how they handle data storage. Ordinals embed all their data directly onto individual satoshis, which are the smallest units of Bitcoin, thereby increasing the transaction size. In contrast, traditional NFTs store most of their data off-chain and only reference it through a smart contract. Additionally, unlike NFT creators who can earn royalties from secondary sales, creators of Ordinals do not receive such royalties.
2. What functionalities do Bitcoin Ordinals offer?
Bitcoin Ordinals introduce a capability to the Bitcoin network that allows users to embed various types of data directly onto Bitcoin’s smallest units, known as Satoshis. This data can include images, videos, and even memes, thereby enhancing the utility and versatility of Bitcoin transactions.
3. What is the current market value of Bitcoin Ordinals?
As of the latest update, the price of Bitcoin Ordinals (ORDI) is approximately USD $44.79, with a 24-hour trading volume of $317.02 million. The ORDI token has seen a recent increase of 11.93% in its value over the last 24 hours. However, it is currently trading at 27.77% below its 7-day high of $62.01 and is 14.87% above its 7-day low of $38.99. The circulating and maximum supply of ORDI tokens is capped at 21 million.
4. What exactly are Bitcoin Ordinals inscriptions?
Bitcoin Ordinals inscriptions are a new trend that involves permanently embedding data such as code, images, audio, and text files into the Bitcoin blockchain. Each inscription is associated with a specific ordinal, which identifies a unique satoshi. This allows for distinct and individualized data to be stored in each transaction unit of Bitcoin.
Table of Contents
References
[1] – https://dydx.exchange/crypto-learning/bitcoin-ordinals
[2] – https://chain.link/education-hub/ordinals-bitcoin-nfts
[3] – https://www.investopedia.com/what-are-bitcoin-ordinals-7486436
[4] – https://www.thestreet.com/crypto/innovation/bitcoin-fees-spiking-ordinals-reshape-future-of-money
[5] – https://thebloggingbuddha.com/bitcoin-ordinals-vs-ethereum-nfts/
[6] – https://hackernoon.com/bitcoin-ordinals-explained-a-comprehensive-guide
[7] – https://decrypt.co/resources/what-are-ordinals-a-beginners-guide-to-bitcoin-nfts
[8] – https://research.aimultiple.com/controversy-around-ordinals/
[9] – https://help.magiceden.io/en/articles/7241924-magic-eden-bitcoin-ordinals-a-comprehensive-guide-to-getting-started
[10] – https://blockworks.co/news/ordinals-impact-on-bitcoin-network
[11] – https://medium.com/@OneBlockplus/a-comparison-between-ordinals-nft-and-traditional-nft-2720da7efc81
[12] – https://cointelegraph.com/learn/bitcoin-ordinals-vs-ethereum-nfts
[13] – https://www.xverse.app/blog/bitcoin-ordinals-use-cases
[14] – https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/diverse-use-cases-bitcoin-ordinals-joe-sticca-vl1se
[15] – https://medium.com/@nftfnofficial/beyond-bitcoin-exploring-the-use-cases-of-ordinals-nftfn-c79e6d17028a
[16] – https://www.forbes.com/sites/digital-assets/2023/06/26/bitcoin-nfts-guide-how-to-get-started-with-ordinals/
[17] – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LO9Fj1SzqwM
[18] – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nKYdrR9g0L4
[19] – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nFpqSOrmxF0
[20] – https://medium.com/coinmonks/top-bitcoin-ordinals-and-runes-projects-heres-how-you-can-launch-your-own-ordinals-collection-defefe158fd8
[21] – https://flagship.fyi/outposts/bitcoin-economy/top-10-bitcoin-ordinals-projects/
[22] – https://www.coingecko.com/learn/top-ordinal-projects
[23] – https://www.tokenmetrics.com/blog/bitcoin-ordinal-nft
[24] – https://fortune.com/crypto/2024/01/30/bitcoin-fight-over-ordinals-nfts/
[25] – https://ordinalrevolution.com/the-ripple-effect-of-bitcoin-ordinals-inscriptions-on-the-crypto-ecosystem/
[26] – https://www.coindesk.com/consensus-magazine/2023/02/17/bitcoin-ordinals-can-lift-the-entire-crypto-ecosystem/
[27] – https://alexablockchain.com/bitcoin-ordinals-innovation-or-disruption/
[28] – https://www.forbes.com/sites/digital-assets/2024/02/22/bitcoin-ordinals-may-push-fees-above-mining-rewards-in-2024/
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered financial or investment advice. Always do your own research and consult with a professional before making any investment decisions. Hash Herald is not responsible for any loss or profits in the crypto markets.